THE ORIGINS OF
TOMATO
The tomato originates from tropical America and Peru in particular. The Incas took control of
the Andean plateaus from the 12th to the 16th century, at that time appeared its name “Tomalt” for this fruit. It was then that the Spanish conquerors discovered this fruit, which was no bigger than our cherry tomatoes.
From Seville, where botanists were experimenting with the discoveries of the New World, the invading Moors did not hesitate to spread this fruit throughout the Mediterranean basin.
The tomato has long been considered an aphrodisiac (1544: the Italian herbalist Pierandrea Matthioli calls it “pomi’doro” or golden apple which he classifies with mandrake. As a result, the tomato is taken as a sexual stimulant and is called “love apple”).
Lycopersicum in Latin “Pêche de loup”, to which the adjective esculentum was added in the 18th century to rebalance its reputation. For England, John Gerard, an English physicist and botanist, says that tomatoes are toxic and only recommend their use in pharmacology. As a result, it was not until 1728 that a few quarters were added to the soups.
In the United States, puritans also displayed mistrust for this fruit of sin by relying on Mattioli’s texts. But in 1806, the American Gardener’s Calendar stated that tomatoes enhanced the taste of sauces and soups. Thomas Jefferson also defends this fruit by planting it in his Monticello garden. In 1834, Dr. John Bennet praised the virtues of tomatoes and with the articles in the New York Times, it was a success. In 1837 “tomato pills” and other miracle cures appeared, in fact he discovered this new source of vitamins.
In fact, it was a judgment of the Supreme Court in 1893 that classified tomatoes in vegetables, whereas in botany it was a fruit. Then came the transition to its raw consumption (sandwich, salad…) and to other epics such as ketchup
THE VARIETIES OF TOMATOES
The tomato is the first vegetable consumed in France. Its classification is mainly done by its different forms:
- The round tomato, is well graded, of a beautiful red and of an irreproachable pace.
- The elongated tomato (Roma or Olivette) is oblong, pulpy and juicy and is ideal for sauces and coulis.
- The ribbed tomato (Marmande) becomes a particular feature of some displays.
- The trusses of tomatoes are particular in the varieties used, which must lead to simultaneous ripening of the 6 to 7 fruits of the trusses.
- The cherry tomato is the curiosity of the aperitif.
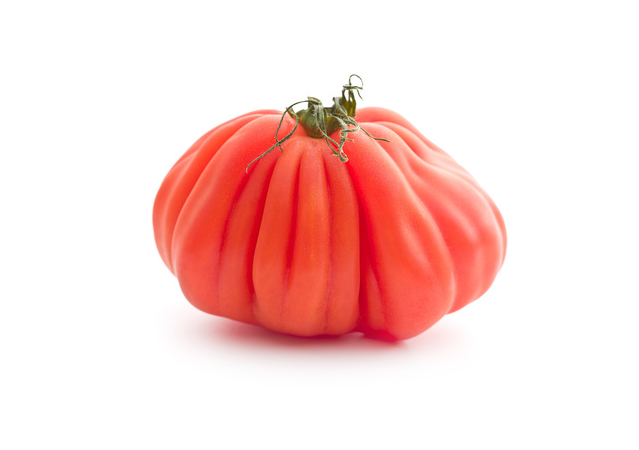

HOW TO CHOOSE TOMATO
The tomato must be bright, fleshy with a smooth, tight skin and a fragrant stalk.
The firm tomatoes will be used for salads while the tomatoes on sale or category II will be used to make sauces. Gratins and stuffed tomatoes require large size tomatoes. It is advisable to take two medium tomatoes for stuffed tomatoes and count 90g of tomatoes per person for a salad. For the coulis, you can take 2 to 3 Kg of tomatoes.
HOW TO STORE AND COOK
TOMATO
Wash the tomatoes before eating them. Tomatoes can be stored at room temperature or in the refrigerator.
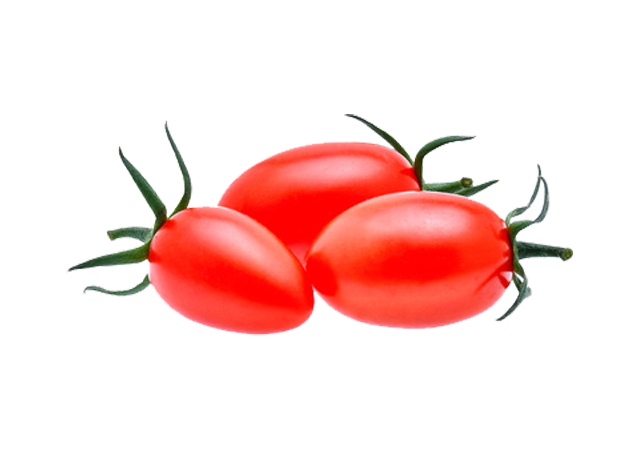


TOMATO’S HEALTH PROPERTIES
The tomato has many virtues, especially as an aperitif. Indeed, it stimulates digestive secretions and allows a better assimilation of the meal. Appreciated by all, it can even be eaten by people with fragile intestines by choosing varieties
with few seeds and dipping the tomatoes in boiling water for a minute to peel them. Organic acids and minerals provide balance to the body. In addition, cell aging is slowed down by the combination of antioxidant carotenoids such as lycopene, which pigments bright red tomatoes.


